Control and Instrumentation Cables
Introduction
Instrumentation cables are specialized cables designed for transmitting low-level electrical signals in instrumentation, control, and communication systems. They are crucial in industrial settings for ensuring accurate data transmission, maintaining signal integrity, and enabling reliable control processes.
Key Characteristics of Instrumentation Cables
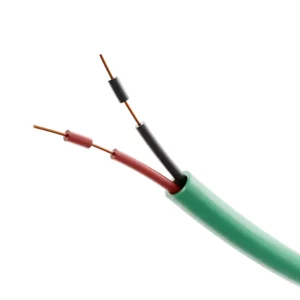
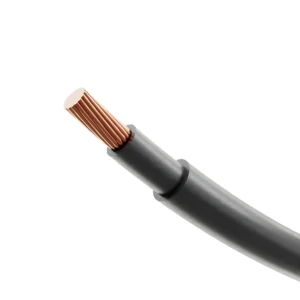
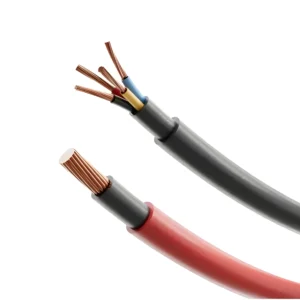
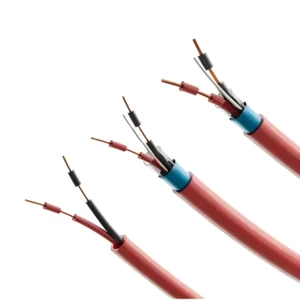
- Conductors: Made from plain or tinned copper for excellent conductivity. These conductors can be single or multi-stranded, depending on the required flexibility and application.
- Insulation: Insulation materials such as PVC, PE, or XLPE are selected based on factors like temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and mechanical durability.
- Shielding: Instrumentation cables often feature shielding, such as braided, foil, or a combination of both, to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure signal clarity.
- Pairs/Triads: These cables contain twisted pairs or triads to minimize crosstalk and improve noise rejection, which is essential for accurate signal transmission.
- Standards and Ratings: ASH Instrumentation cables are manufactured according to industry standards (BS EN 50288-7, UL 13, UL 2250, UL 1277, and IEC). They are rated for various environmental conditions, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of industrial applications.
Applications
Instrumentation cables are used in various settings, including process control, automation systems, data acquisition, and communication networks. They are essential in industries like oil and gas, manufacturing, and power generation for maintaining the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of modern industrial systems.